- Published on
The Revolution of VoiceAI: From TTS to Real-Time Conversation
- Authors

- Name
- K B Rahul
- @kbrahul_
The Revolution of VoiceAI
VoiceAI has transformed from robotic-sounding text-to-speech (TTS) systems to emotionally expressive, real-time conversational agents. This shift is driven by advances in deep learning and the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs).
Evolution of Speech Synthesis
Concatenative Synthesis
Early systems pasted together pre-recorded snippets of sounds (diphones). It sounded natural for specific phrases but was limited in vocabulary and emotion.
Parametric Synthesis
Statistical models (HMMs) generated speech parameters. It was flexible but sounded "buzzy" and unnatural.
Neural TTS
Deep learning changed everything. WaveNet (2016) showed that raw audio waveforms could be generated directly. Today, end-to-end models like VITS (Conditional Variational Autoencoder with Adversarial Learning for End-to-End Text-to-Speech) dominate.
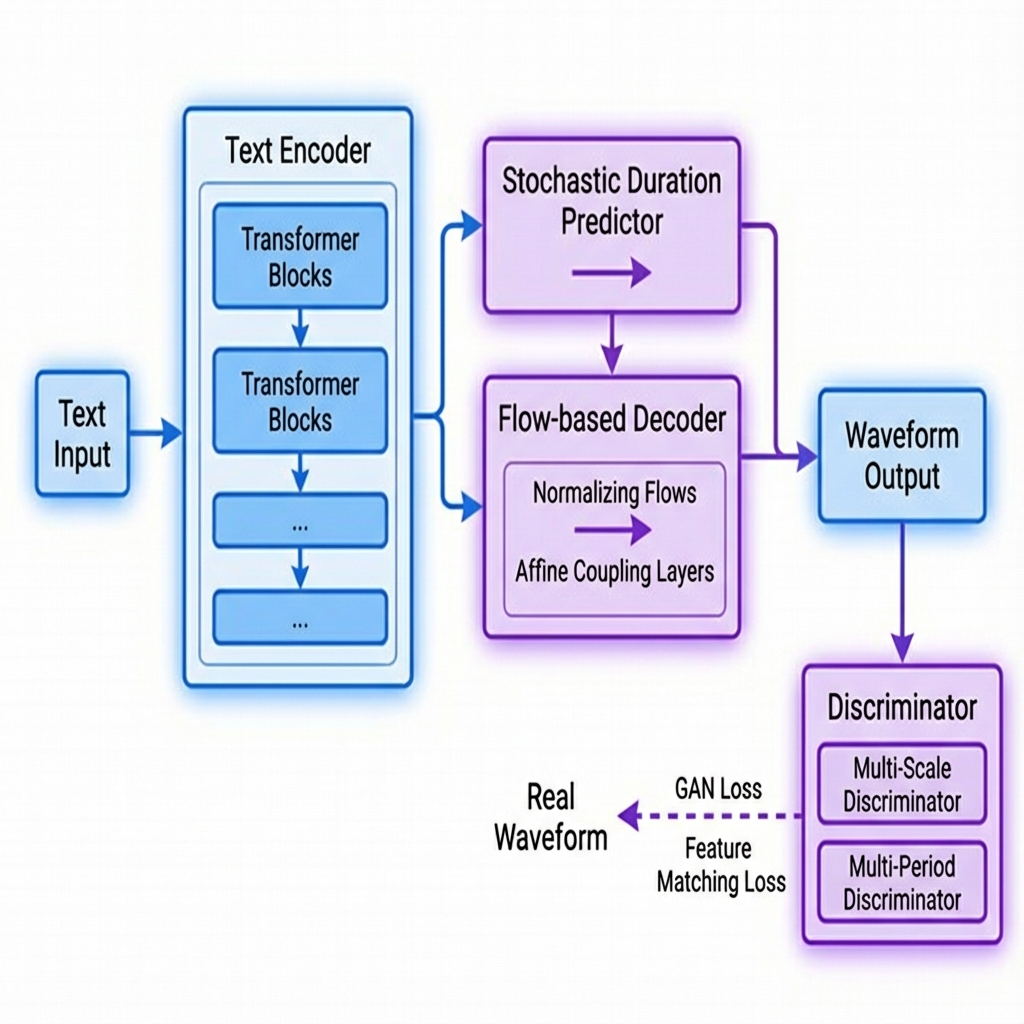
VITS combines the best of both worlds:
- Variational Inference: For expressive and diverse speech generation.
- Normalizing Flows: For complex distribution modeling.
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): For high-fidelity waveform generation.
Unlike previous two-stage pipelines (Acoustic Model -> Vocoder), VITS is fully end-to-end, resulting in faster inference and higher quality.
Voice Conversion & Diffusion Models
Voice conversion allows transforming one speaker's voice into another while preserving linguistic content. Recently, Diffusion Models (like those used in DALL-E) have been applied to audio. They generate speech by iteratively "denoising" a random signal, guided by text or audio conditioning. This allows for zero-shot voice cloning with just 3 seconds of audio.
IMPORTANT
Ethical considerations are paramount in VoiceAI. Consent and transparency are necessary to prevent misuse for impersonation or fraud.
The Future: Real-Time Conversational AI
Combining low-latency ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition), LLMs, and TTS enables real-time voice conversations with AI.
Architecture of a Voicebot
- ASR: Converts user speech to text (e.g., Whisper, Deepgram).
- LLM: Generates a text response (e.g., GPT-4, Llama 3).
- TTS: Synthesizes the response back to speech (e.g., ElevenLabs, proprietary models).
The Latency Challenge
For a conversation to feel natural, the total turn-taking latency should be under 500ms.
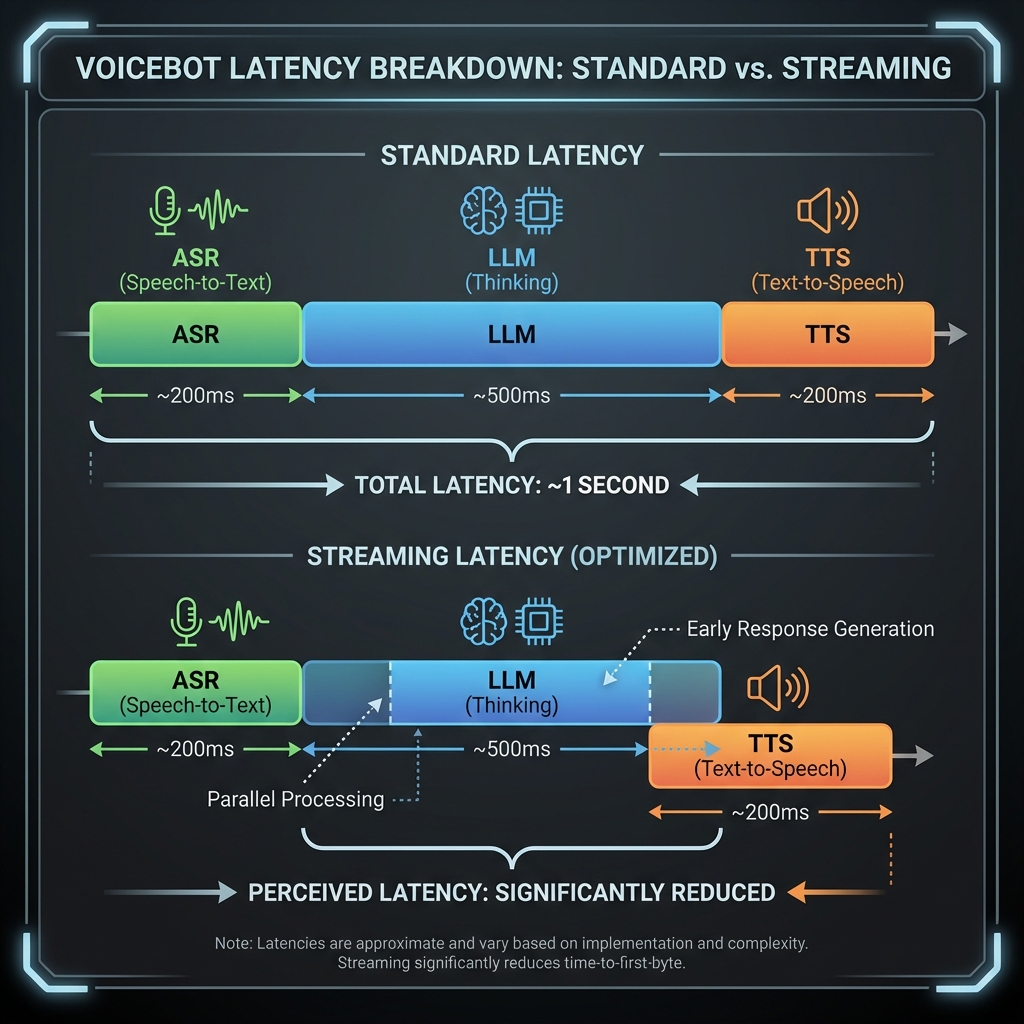
To achieve this, we use Streaming Pipelines:
- ASR Streaming: Send partial text to the LLM as the user speaks.
- LLM Streaming: Send tokens to the TTS engine as they are generated.
- TTS Streaming: Play audio chunks immediately as they are synthesized.
Conclusion
VoiceAI is redefining human-computer interaction. As models become faster and more expressive, voice will likely become the primary interface for technology, moving us closer to the "Her" movie reality.